https://codeforces.com/contest/1637
Dashboard - Codeforces Global Round 19 - Codeforces
codeforces.com
A. Sorting Parts
- 임의의 원소에 대해서 그 원소를 포함하는 앞부분, 그 원소 뒷부분 각각 non-decreasing order 로 정렬한 뒤 전체배열이 non-decreasing 정렬되어있게 만들 수 있는지 판단하는 문제
- a[i] > a[i + 1] 이면 a[i] 를 기준으로 잡으면 만들 수 있다. 그런 경우가 없으면 불가능.
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> a(N);
for (auto& e: a) {
cin >> e;
}
auto sorted = is_sorted(all(a));
if (sorted) {
cout << "NO\n";
} else {
cout << "YES\n";
}
}
}
B. MEX and Array
문제요약
배열 b1, ..., bk 를 c 개의 segment로 나누는 partition에 대해
cost of partition = c + sum(mex(segment[i])) = sum(1 + mex(segment[i]))
value of array = max(cost of partition)
일 때,
입력 배열의 모든 subsegment 에 대해 value 의 합을 구해라
풀이1.
가정: 길이 k 의 segment b1,..., bk 의 cost 기여분은 segment b1, segment b2, ... segment bk 의 cost 기여분의 합보다 작거나 같다. 즉, 세그먼트를 길이 1 segment 로 나눌때 cost 가 최대이다.
증명
- b1...bk 중 0 이 있을 때
- b1...bk 중 0 이 없을 때
1번 경우.
b1...bk 의 cost = 1 + mex <= 1 + k (k개 원소이므로 mex 최댓값이 k)
길이 1로 파티션 했을 때 cost = k + (zerocnt) * 1
이 때 zerocnt >= 1 이므로 길이 1 파티션의 cost 가 더 크다.
2번 경우.
b1...bk의 cost = 1 + 0 = 1
길이 1로 파티션 했을 때 cost = k + 0
k >= 1 일 때 길이 1 파티션 cost 가 크거나 같다.
어떤 segment 의 cost 보다 그 segment 를 길이 1 파티션했을때가 cost 가 더 크거나 같다는 것을 증명했다.
segment 를 파티션하는 방법중 cost 가 제일 큰 파티션방법에 길이가 1 보다 큰 segment 가 있다고 가정하면
그 segment 의 cost 는 그 segment 를 1로 파티션한 cost 보다 작거나 같으므로 cost 가 최대라는 것에 모순.
따라서 segment 를 파티션하는 방법중 cost 가 제일큰 파티션방법은 길이 1로 파티션하는 것이다.
코드
- sum(value of all subsegment) = sum(subsegment length + 1 * zerocnt)
- 시간복잡도: O(N)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> a(N);
long long answer = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
answer += 1LL * i * (N - i + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] == 0) {
answer += 1LL * (i + 1) * (N - i);
}
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}
풀이2.
dp[l][r] = value of arr[l...r]
= max(1 + mex(arr[l...r]), max(dp[l][l + c] + dp[l + c + 1][r]))
코드
- 시간복잡도: O(N^4)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> a(N);
for (auto& e: a) {
cin >> e;
}
auto getMEX = [&](vector<int> arr) {
sort(all(arr));
int mex = 0;
for (auto e: arr) {
if (e == mex) {
++mex;
} else {
break;
}
}
return mex;
};
vector<vector<long long> > dp(N, vector<long long> (N, -1));
function<long long(int, int)> f = [&](int l, int r) {
long long& ret = dp[l][r];
if (ret != -1) {
return ret;
}
vector<int> tmp(a.begin() + l, a.begin() + r + 1);
ret = 1 + getMEX(tmp);
for (int i = l; i < r; ++i) {
ret = max(ret, f(l, i) + f(i + 1, r));
}
return ret;
};
long long answer = 0;
for (int l = 0; l < N; ++l) {
for (int r = l; r < N; ++r) {
answer += f(l, r);
}
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}C. Andrew and Stones
문제요약
operation:
1 <= i < j < k <=n 인 i, j, k 선택
j 에서 i, j 로 1개씩 옮김
operation 최소로 사용해서 양 끝말고는 all 0 만들기
풀이
odd: o, even: e
처음 끝 사이 배열에 대해서
- 길이 1 이고 홀수면 불가능
- 짝수가 하나라도 껴있는 꼴이면 가능
- e o o o -> 0 e o o -> ... -> 0 0 0 0
- 모두 홀수인데 3 이상인게 하나라도 있으면 위의 꼴로 만들 수 있음
- o 3 o -> e o e -> ... -> 0 0 0
- 필요한 operation 횟수 >= sum(ceil(a[i] / 2))
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> a(N);
for (auto& e: a) {
cin >> e;
}
if ((N == 3 && a[1] & 1) || (*max_element(a.begin() + 1, a.end() - 1) == 1)) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
long long answer = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N - 1; ++i) {
answer += a[i] + 1 >> 1;
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}D. Yet Another Minimization Problem
풀이
수식 정리하면
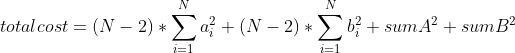
앞 두 항의 합은 a, b 원소 스왑해도 일정. totalcost 는 뒤 두항에 따라 달라짐
sumB = totalSum - sumA
원소 값의 범위가 1~100 이고 갯수는 100 이므로 sumA 가 될 수 있는 최댓값은 100 * 100
dp[i][sum]: operation 후 가능한 a 에 대하여 i 열까지 합이 sum 이 가능하면 true
dp[i][sum] = dp[i - 1][sum - a[i]] || dp[i - 1][sum - b[i]]
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
if (N == 1) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "0\n";
continue;
}
int maxSum = 100 * 100;
vector<long long> a(N), b(N);
long long answer = 0;
long long totalSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> a[i];
answer += 1LL * (N - 2) * a[i] * a[i];
totalSum += a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> b[i];
answer += 1LL * (N - 2) * b[i] * b[i];
totalSum += b[i];
}
vector<vector<int> > dp(N, vector<int> (maxSum + 1, false));
dp[0][a[0]] = dp[0][b[0]] = true;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = maxSum; j >= 0; --j) {
if (j - a[i] >= 0) dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1][j - a[i]];
if (j - b[i] >= 0) dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1][j - b[i]];
}
}
long long tmp = 1e18;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxSum; ++i) {
if (dp[N - 1][i]) {
tmp = min(tmp, 1LL * i * i + 1LL * (totalSum - i) * (totalSum - i));
}
}
cout << answer + tmp << '\n';
}
}E. Best Pair
cntX, cntY (cntY <= cntX), x 에 대해 y는 가장 큰 값(x != y && bad pairs 가 아닌) 만 보면 됨
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N, M;
cin >> N >> M;
map<int, int> cnt;
vector<long long> a(N);
for (auto& e: a) {
cin >> e;
cnt[e]++;
}
set<pair<int, int> > bad;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
bad.insert({x, y});
bad.insert({y, x});
}
long long answer = 0;
set<int> cntSet;
vector<vector<int> > v(N + 1);
for (auto [num, cnt_]: cnt) {
cntSet.insert(cnt_);
v[cnt_].push_back(num);
}
for (auto& e: v) {
reverse(all(e));
}
for (auto rit = cntSet.rbegin(); rit != cntSet.rend(); ++rit) {
for (auto rit2 = rit; rit2 != cntSet.rend(); ++rit2) {
for (auto x: v[*rit]) {
for (auto y: v[*rit2]) {
if (x != y && bad.find({x, y}) == bad.end()) {
answer = max(answer, 1LL * (x + y) * (*rit + *rit2));
break;
}
}
}
}
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}'PS > Codeforces' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #774 (Div. 2) (코포 774 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.03.19 |
|---|---|
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #773 (Div. 2) (코포 773 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.27 |
| [코드포스] Educational Codeforces Round 123 (Rated for Div. 2) (에듀코포 123 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.24 |
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #772 (Div. 2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.22 |
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.22 |