https://codeforces.com/contest/1642
Dashboard - Codeforces Round #773 (Div. 2) - Codeforces
codeforces.com
A. Hard Way
더보기
풀이
- $y = 0$ 에 도달할 수 없는 점이 존재 하려면 세 점중 y 값이 최소가 아닌 두 점이 이루는 변이 x 축과 평행해야 하고 그 변의 길이가 답이 된다
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
vector<pair<long long, long long> > p(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
cin >> p[i].first >> p[i].second;
}
if (p[0].second > p[1].second) swap(p[0], p[1]);
if (p[0].second > p[2].second) swap(p[0], p[2]);
long double answer = 0.0;
if (p[1].second == p[2].second) {
answer = abs(p[1].first - p[2].first);
}
cout.precision(9);
cout << fixed << answer << '\n';
}
}
B. Power Walking
더보기
풀이
- $k = n$ 일 때 힘의 합은 $k$
- $k = n - 1$ 일 때 서로 다른 두개를 합치면 합은 이전 합과 같고, 같은 두개 합치면 이전합 + 1
- 같은 게 있으면 같은 것들 부터 합치자
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
map<int, int> a;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int num;
cin >> num;
++a[num];
}
int d = 0;
for (auto [num, cnt]: a) {
if (cnt >= 2) d += cnt - 1;
}
vector<int> answer;
int k = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if (d) {
answer.push_back(k);
--k;
d--;
} else {
answer.push_back(k);
}
}
reverse(all(answer));
for (auto e:answer) {
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
}
C. Great Sequence
더보기
풀이
- 제일 큰 distinct 원소부터 매칭이 되면 넘어가고 수를 추가해야되면 그 수만큼 추가해준다
코드
- 시간복잡도: $O(NlogN)$
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
long long N, X;
cin >> N >> X;
map<long long, long long> m;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int num;
cin >> num;
++m[num];
}
int answer = 0;
for (auto rit = m.rbegin(); rit != m.rend(); ++rit) {
if (rit -> second == 0) continue;
if (rit -> first % X == 0) {
auto it = m.lower_bound(rit -> first / X);
if (it != m.end() && it -> first == rit -> first / X && it -> second > 0) {
int tmp = min(rit -> second, it -> second);
it -> second -= tmp;
rit -> second -= tmp;
}
if (rit -> second > 0) {
answer += rit -> second;
rit -> second = 0;
}
} else {
answer += rit -> second;
}
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}
D. Repetitions Decoding
더보기
풀이
- operation 해도 각 문자들의 parity 가 유지되므로 홀수 개수인 문자가 존재하면 불가능하다
- 문자열 $c_1c_2c_3...$ 에 $c_3, c_2, c_1$ 을 뒤에 넣으면 $c_1c_2c_3c_3c_2c_1c_3c_2c_1...$ 로 만들 수 있다
- 앞에 부분은 tandem repeat 으로 빼놓고 뒷부분은 원래 문자열의 앞부분을 reverse 한것과 같다.
- 이 작업으로 문자열 뒷부분이 원래 문자열을 정렬한 상태로 두면 그 문자열은 순서대로 각 문자의 개수만큼 tandem repeat 을 이룬다
- $c_1c_1c_2c_2c_2c_2c_3c_3...$
코드
- 시간복잡도: $O(N^2)$
- 정렬하는데 각 원소마다 reverse 2번: $O(N)$
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int TC; cin >> TC;
while (TC--) {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<long long> a(N);
map<int, int> cnt;
for (auto& e: a) {
cin >> e;
++cnt[e];
}
bool no = false;
for (auto e: cnt) {
if (e.second & 1) {
no = true;
break;
}
}
if (no) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
vector<long long> sortedA(a);
sort(all(sortedA));
int start = 0;
vector<pair<int, int> > operation;
vector<int> t;
auto swapWithFirst = [&](int i) {
if (i == 0) return;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
operation.push_back({start + j + i + 1, a[j]});
}
reverse(a.begin(), a.begin() + i + 1);
t.push_back(i + 1 << 1);
start += i + 1 << 1;
};
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; --i) {
if (a[i] != sortedA[i]) {
auto it = find(a.begin(), a.begin() + i, sortedA[i]);
if (it != a.begin()) {
swapWithFirst(it - a.begin());
}
swapWithFirst(i);
}
}
for (auto e: cnt) {
t.push_back(e.second);
}
cout << operation.size() << '\n';
for (auto [p, c]: operation) {
cout << p << ' ' << c << '\n';
}
cout << t.size() << '\n';
for (auto e: t) {
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
}
E. Anonymity Is Important
더보기
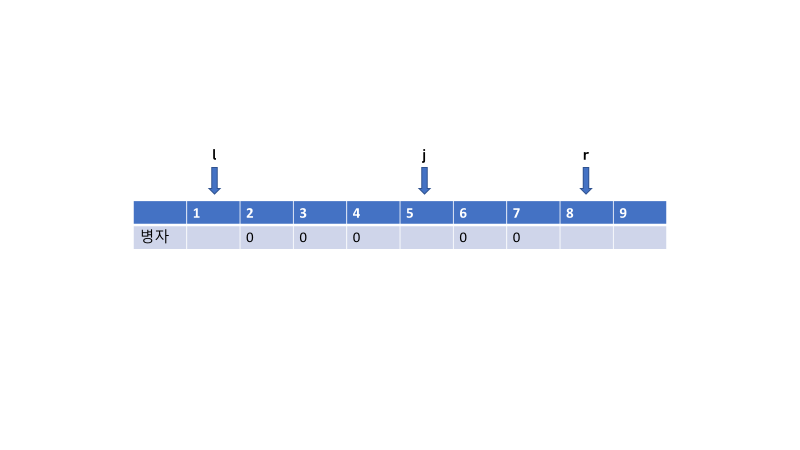
예제 그림
풀이
- 병자 후보를 set 으로, 0 l r 1 쿼리를 세그먼트 트리로 관리
- t = 0
- x = 0
- set 에서 l 부터 r 까지 범위에 있는것들 다 지움 ($O(NlogN)$)
- x = 1
- l 노드 값 min(t[N + l], r) 로 업데이트
- x = 0
- t = 1
- 병자 후보에 없으면 병 안걸림
- 병자 후보 set 에서의 j 의 위치 앞, 뒤에 있는 후보를 l, r 이라고 하면
- l + 1, j 구간의 오른쪽 구간 최소값이 뒤 후보값인 r 보다 작으면 그 구간에 j가 1을 결정하므로 병자임을 확정할 수 있다. 그 외 경우엔 여러 원소가 있으므로 결정할 수 없다.

코드
- 시간복잡도: $O(NlogN + QlogN)$
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define rall(v) (v).rbegin(), (v).rend()
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int N, Q;
cin >> N >> Q;
set<int> can;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) can.insert(i);
vector<int> t(2 * N, 1e9);
auto update = [&](int p, int val) {
for (t[p += N] = val; p > 1; p >>= 1) t[p >> 1] = min(t[p], t[p ^ 1]);
};
auto query = [&](int l, int r) {
int ret = 1e9;
for (l += N, r += N; l < r; l >>= 1, r >>= 1) {
if (l & 1) ret = min(ret, t[l++]);
if (r & 1) ret = min(ret, t[--r]);
}
return ret;
};
while (Q--) {
int t2, l, r, x, j;
cin >> t2;
if (t2 == 0) {
cin >> l >> r >> x; --l; --r;
if (x == 0) {
for (auto it = can.lower_bound(l); it != can.end() && r >= *it;) {
can.erase(it);
it = can.lower_bound(l);
}
} else {
update(l, min(t[l + N], r));
}
} else {
cin >> j; --j;
if (!can.count(j) || !can.size()) {
cout << "NO\n";
continue;
}
int l = 0, r = N;
auto it = can.lower_bound(j);
if (it != can.begin()) l = *prev(it) + 1;
if (next(it) != can.end()) r = *next(it);
cout << (query(l, N) < r ? "YES\n" : "N/A\n");
}
}
}728x90
'PS > Codeforces' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #775 (Div. 2) (코포 775 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
|---|---|
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #774 (Div. 2) (코포 774 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.03.19 |
| [코드포스] Educational Codeforces Round 123 (Rated for Div. 2) (에듀코포 123 딥2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.24 |
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #772 (Div. 2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.22 |
| [코드포스] Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2) 풀이 (0) | 2022.02.22 |